

Implementing basic IPv6 connectivity in the Cisco software consists of assigning IPv6 addresses to individual device interfaces.
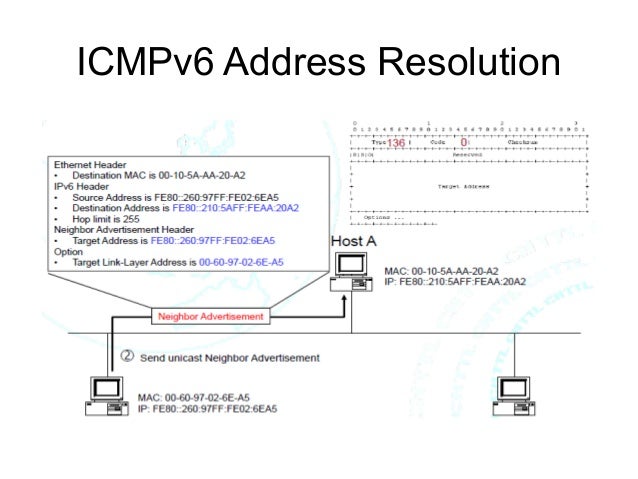
The unlimited address space provided by IPv6 allows Cisco to deliver more and newer applications and services with reliability, improved user experience, and increased security. Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) expands the number of network address bits from 32 bits (in IPv4) to 128 bits, which provides more than enough globally unique IP addresses for every networked device on the planet. Feature Information for IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity.Example: Hostname-to-Address Mappings Configuration.Example: Dual-Protocol Stack Configuration.Example: IPv6 Addressing and IPv6 Routing Configuration.Configuration Examples for IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity.Configuring an Interface to Support the IPv4 and IPv6 Protocol Stacks.
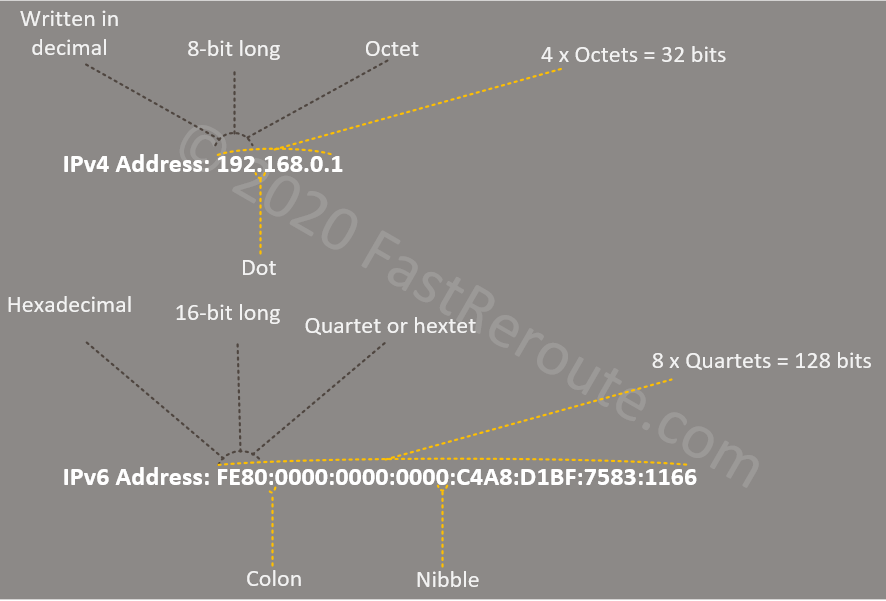
Configuring IPv6 Addressing and Enabling IPv6 Routing.How to Configure IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity.IPv6 on BVI Interfaces for Bridging and Routing.IPv6 for Cisco Software Support for Wide-Area Networking Technologies.Cisco Discovery Protocol IPv6 Address Support.Large IPv6 Address Space for Unique Addresses.Information About IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity.Restrictions for IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity.You can use the both zero and leading zero compression together by following the rules of these compression techniques. IPv6 address with Leading zero compression:Ģ001:1265:0:0:AE4:0:5B:6B0 Both Zero and Leading zero compression If you have all zero in a hextex you can represent this hextex with one zero. In leading zero compression you can eliminate the starting zero(s) from any hextex. Review the example for better understanding.Ģ001:1265::0AE4:0000:005B:06B0 IPv6 Leading Zero Compression In zero compression you can represent group of zeros by one double-colon (::) but you can perform this only once in your IPv6 address, means if you have two group of zeros in your IPv6 address you can use the double-colon only once. These compression rules and methods are as follow: IPv6 address consist of 8 hextets or parts which is normally difficult to remember, therefore there are some compression method, using compression techniques you can represent IPv6 in more understandable and simple way. This is a simple example of IPv6 address, you can see in below figure IPv6 address have eight hextets/parts and each hextet/part consist of 4 digits and of 16bits, while every digits is of 4bits that you can find from above table. Representation of all hexadecimal number/digits in binary form is as follows: Hexadecimal #
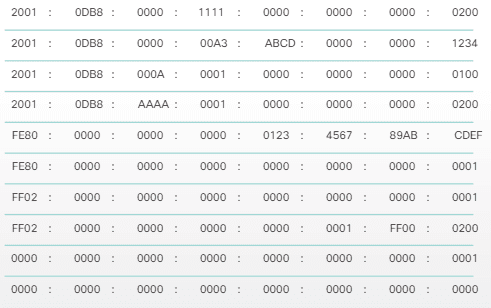
IPv6 addresses are in hexadecimal form, so each digit is of four bits, IPv6 address’s consist of possible digits are 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F. IPv6 address is of 128 bits and represented in eight octets of 16 bits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
